In the late 1970s and early 1980s, a significant shift occurred in the automotive industry as manufacturers sought ways to produce lighter and more cost-effective vehicles. This transformation led to the gradual replacement of timing chains with timing belts. The primary motivation behind this transition was the desire to reduce vehicle weight, which in turn promised increased fuel efficiency. However, as we delve into the world of timing belts, a multitude of questions often arise. Understanding the role of timing belts and knowing when they should be replaced is essential to ensure the smooth operation of your vehicle and to avoid expensive breakdowns. It is worth noting that not all cars are equipped with timing belts; some utilize timing chains, which are making a resurgence in popularity due to their durability. Therefore, it is crucial to consult your vehicle’s manufacturer guide to determine whether your vehicle is equipped with a timing belt or chain.
What does a Timing Belt do?
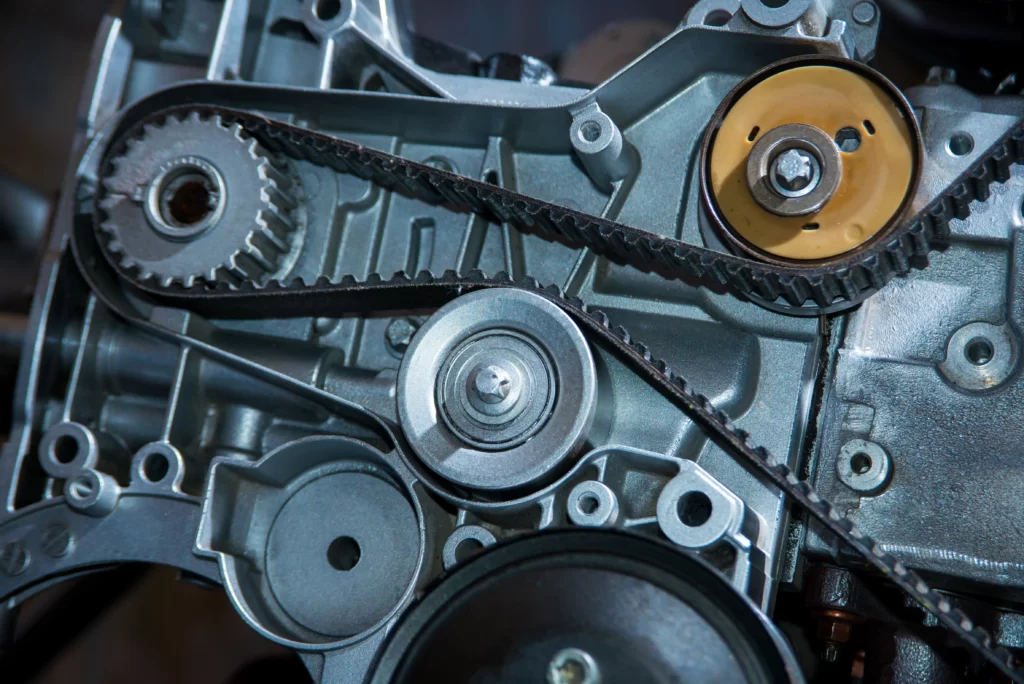
A timing belt plays a pivotal role in your vehicle’s engine system by synchronizing the movement of the camshaft and crankshaft at the correct rate. The crankshaft is responsible for moving pistons during compression and exhaust cycles, while the pistons move downwards during power and intake cycles. Depending on the make and model of your vehicle, the timing belt may also drive essential components such as the water pump, oil pump, and injection pump. Simultaneously, the camshaft controls the opening and closing of valves for the intake and exhaust processes. Proper timing ensures that these valves open and close at the precise moments, allowing fuel to enter the combustion chamber and facilitating compression. If the timing cycle is off, fuel may not enter the cylinder or could escape through an open exhaust valve. Moreover, if the valves do not fully close during compression, a substantial portion of the engine’s power is lost.
When Should It Be Replaced?

A common question among car owners pertains to the replacement interval for timing belts. The conventional wisdom used to be to replace the timing belt every 60,000 miles. However, with advancements in technology and materials, many manufacturers now recommend replacement intervals of up to 100,000 miles. To ensure the longevity and reliability of your vehicle, it is essential to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended replacement interval. Signs of a faulty belt include a loss of power, decreased fuel economy, misfiring, and engine vibrations. Unlike in the past, timing belt noise is no longer a prominent indicator of potential failure, as modern belts are designed to operate quietly. Nevertheless, if you are undertaking other maintenance work that necessitates the removal of the timing belt cover and belt, it is advisable to replace the belt. When the water pump requires replacement, the belt must be removed in most vehicles. Reinstalling a used belt is discouraged, as it tends to stretch over time, making precise timing challenging. The primary cost of timing belt or water pump replacement lies in labor, making it a wise choice to invest in a new belt. This same principle applies when replacing a timing belt, as it is prudent to consider replacing the water pump at the same time, particularly if it is nearing the end of its expected lifespan. This approach can save you money by reducing the labor costs associated with a separate service.
Consequences of a Timing Belt Failure
In the event of a timing belt failure, the outcome largely depends on the type of engine installed in your vehicle. Engines can be classified as either interference or non-interference engines. Interference engines provide slightly more power due to increased compression, making them common in smaller vehicles. In such engines, the valves extend further into the cylinder, which means that if the timing is incorrect, the valve may not be out of the way when the piston moves upward. When a timing belt breaks in an interference engine, one or more valves may be left open. As a result, when the pistons move upwards, they forcefully collide with the open valves, leading to varying degrees of damage. In the best-case scenario, you may have some broken valves and damaged pistons. In the worst-case scenario, the valves and rods can breach the engine cover, and pistons may even puncture the oil pan if the crankshaft twists or breaks during the process, rendering the engine irreparable.

While determining whether your engine is interference or non-interference can be done through research, it is crucial to note that even non-interference engines are not immune to costly repairs if the timing belt fails. In such cases, timing belt replacement becomes a critical maintenance task. Accessing the timing belt for inspection and replacement typically requires the expertise of a qualified repair shop, as it involves removing multiple engine components. If you observe any signs of wear, such as cracks or worn-out teeth on the timing belt, it should be replaced promptly. Stretching or oil contamination are also clear indicators that a new belt is necessary. For used cars without records of the belt replacement, scheduling an inspection with a trusted automotive service center is recommended. Meineke Car Care Centers, staffed with experienced technicians, can address your questions regarding auto maintenance, timing belt symptoms, and noise. If you’re uncertain about the timing belt replacement schedule for your vehicle, Meineke has the answers you need.
Consulting a qualified automotive service center, such as Full Circle Auto Service servicing the O’Fallon IL area, can provide you with expert guidance on timing belt maintenance and ensure the continued reliability of your vehicle.